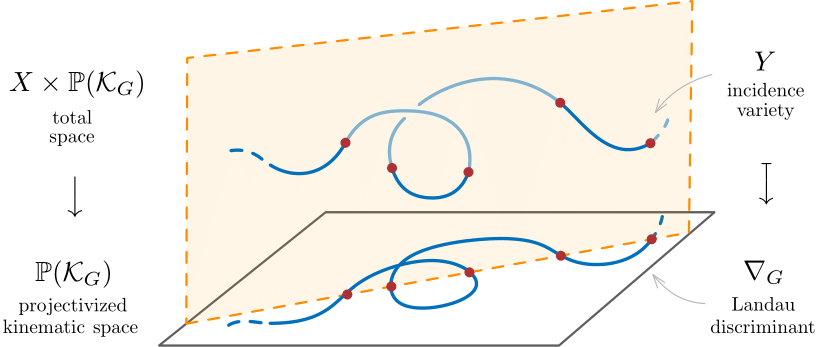
Landau Discriminants
ABSTRACT: Scattering amplitudes in quantum field theories have intricate analytic properties as functions of the energies and momenta of the scattered particles. In perturbation theory, their singularities are governed by a set of nonlinear polynomial equations, known as Landau equations, for each individual Feynman diagram. The singularity locus of the associated Feynman integral is made precise with the notion of the Landau discriminant, which characterizes when the Landau equations admit a solution. In order to compute this discriminant, we present approaches from classical elimination theory, as well as a numerical algorithm based on homotopy continuation. These methods allow us to compute Landau discriminants of various Feynman diagrams up to 3 loops, which were previously out of reach. For instance, the Landau discriminant of the envelope diagram is a reducible surface of degree 45 in the three-dimensional space of kinematic invariants. We investigate geometric properties of the Landau discriminant, such as irreducibility, dimension and degree. In particular, we find simple examples in which the Landau discriminant has codimension greater than one. Furthermore, we describe a numerical procedure for determining which parts of the Landau discriminant lie in the physical regions. In order to study degenerate limits of Landau equations and bounds on the degree of the Landau discriminant, we introduce Landau polytopes and study their facet structure. Finally, we provide an efficient numerical algorithm for the computation of the number of master integrals based on the connection to algebraic statistics. The numerical algorithms used in this work are implemented in the open-source Julia package Landau.jl.
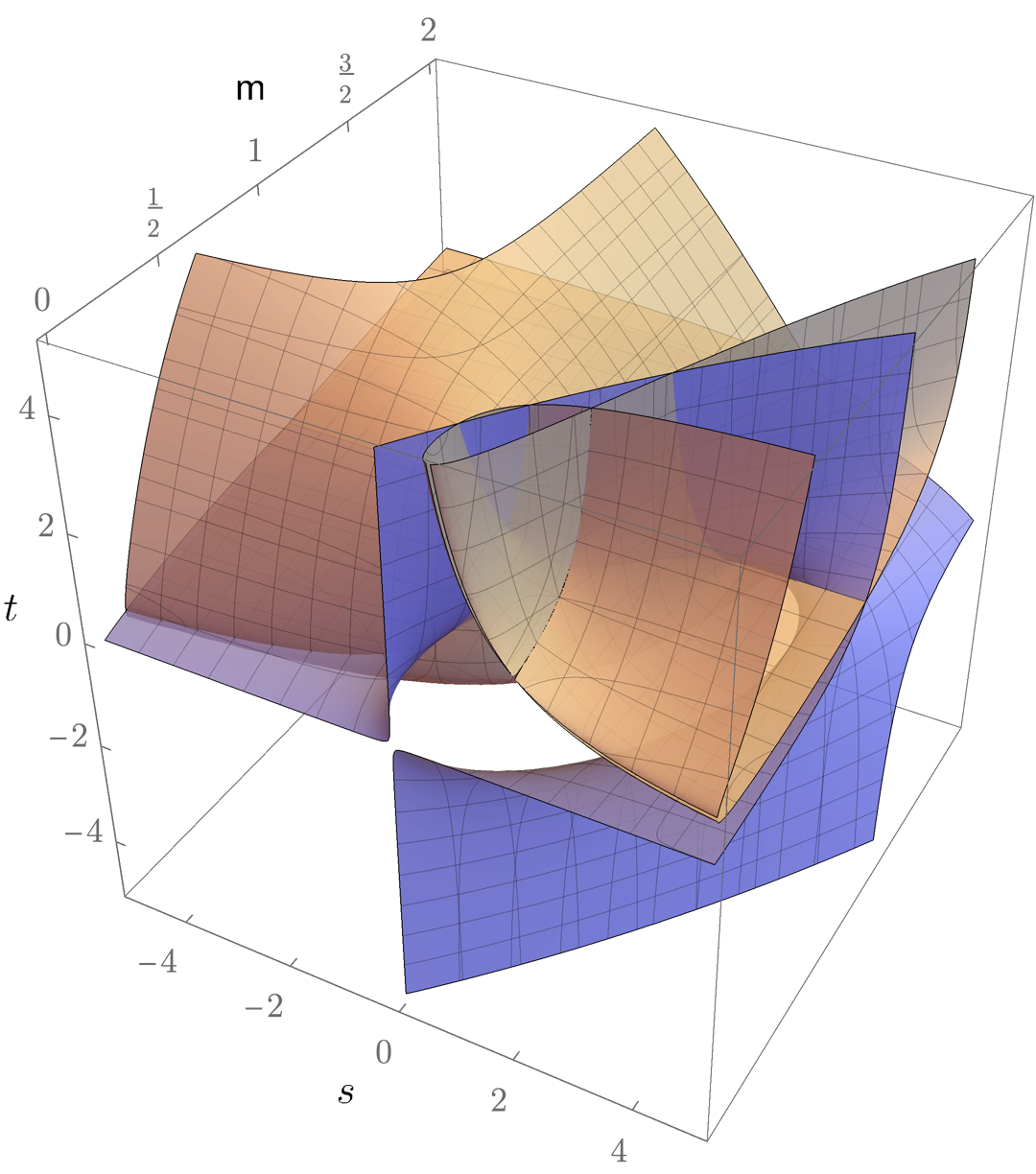
As an illustration, the following figure shows the Landau discriminant for the double box Feynman diagram corresponding to the three dimensional subspace corresponding to equal internal and external masses.
As indicated above, our numerical methods are implemented julia. The packages is called Landau.jl. It makes use of HomotopyContinuation.jl (v2.6.0). The following Jupyter notebook illustrates how our Julia code, which may be downloaded here julia_code.zip, can be used.
You can also run our jupyter notebook online:
All discriminants computed and discussed in Section 3.3.2 of the paper can be reproduced using this code, and they can be downloaded in txt format here discriminants_Sec332.zip.
The paper also presents some symbolic elimination methods for computing Landau discriminants. The code in Macaulay2 used for creating Table 1 can be downloaded here code_Table1.m2.
Project page created: 15/09/2021
Project contributors: Sebastian Mizera, Simon Telen
Corresponding author of this page: Simon Telen, Simon.Telen@mis.mpg.de
Software used: Julia (Version 1.5.2), Macaulay2 (Version 1.13)